1.Information system
Law 100 in its decree 2309 establishes a mandatory quality assurance system whose basis is information systems, making the clinical history the vital instrument.This objectively reflects the care provided and the results obtained.The clinical record is the main vehicle for communicating information about the patient between members of the health team and an important tool for evaluating and measuring the quality of health services.
For this reason, for six years, the quality of nursing records has been evaluated, classifying them as adequate or inadequate based on a checklist that describes all the steps for correctly completing the record.The records evaluated are: nursing notes, medication administration, fluid control, checklist of nursing activities as well as those specific to the Emergency Department and Delivery Room.For this year, the completion of records in all services was unified and the evaluation instrument was modified so that it allows us to know the exact cause of the record classified as incomplete.Monitoring is done daily and the report is done monthly.The goal was set for 90% of these to be completed correctly.Of the records evaluated in 2001 (n= 69,446) the overall evaluation was 94.2% and in 2002 (n= 63,364) it was 93%.At the individual level, the only registry that did not meet the goal was the medication registry.The results are substantially the same as the previous year.However, this permanent review, in addition to ensuring adequate records, has decreased the number of glosses with nursing responsibility due to problems with the records in the clinical history.
1.1 Digital hospital
One of the most ambitious projects that the institution has developed since its creation is the digitalization of the hospital as a tool for safe care.Throughout the year, the processes were reviewed and adapted to the acquired software, developing the new requirements for nursing care.The implementation of this tool will be of great benefit to nursing since it will eliminate transcription errors due to illegibility and will allow the verification of interactions, contraindications and dosage, while contributing to the timeliness of care by eliminating intermediate steps.
2.Evaluation and control system
Implementing evaluation and control systems today is absolutely necessary for the success of any management.This formulation of indicators corresponds to the strategic direction process proposed by the institution in which, chronologically, the vision, mission, principles, objectives, strategies and ultimately, as an operational element, the quality indicators were established.Thanks to the fact that the department has standardized processes, indicators can be used to evaluate the quality of care.When an indicator is activated it does not necessarily mean a quality failure, however it requires an analysis of the process and if the final judgment is a quality problem, corrective measures are implemented and subsequent verification of their effectiveness.
To support the management of the nursing department of our Institution, there are three categories of indicators:
1 Intrinsic Quality
2 User Satisfaction
3 Personal
2.1.Indicators of intrinsic quality of the healthcare area
They measure specific processes of care for patients chosen for their frequency, importance or high risk.
2.1.1.Nosocomial infection
The incidence of infectious processes (infected patients/# discharges) acquired in the institution was 1.7%, slightly higher than one year 2001 (1.2%) being well below the international standard (14%).The distribution of these infections according to the anatomical site shows that surgical site infection occupied 29.2%, bacteremia 24.9%, respiratory tract infections 15.6%, clinical sepsis 11.8%, gynecological-obstetric infections 5.4%, urinary tract 4.8%, cardiovascular system 2.7%, candidemias 1.6%, soft tissues and gastrointestinal 1.34% and less than 1% musculoskeletal and sense organs.Additionally, 153 alcohol gel dispensers were installed in rooms, hospitalization services and outpatient consultation areas to facilitate and encourage permanent hand washing.
It is important to highlight that by services, the intensive care units Adults account for 26% of the institution’s nosocomial infections, pediatric services account for 26.5%, and hospitalization services (2nd, 3rd, and 4th) including patients from the surgical site infection (ISO) program for outpatient surgery, contribute 47.5%.
2.1.2 Incidence of phlebitis secondary to peripheral venipuncture
During 2001, 25,361 venipunctures compared to 2000, which were 20,778. In 2002, #29,411 were registered, which implies an increase of 4,050 records.A follow-up sheet is initiated for each venipuncture, recording the identification of the patient, the venipuncture, follow-up dates and the cause of withdrawal in order to determine the variables that may influence the presence of phlebitis.It is worth highlighting that the complete completion of this document ensures the reliability and significance of the information collected.
The goal established for this year was to keep phlebitis no higher than 5% and that 80% of these were between grades I and II.The incidence of phlebitis, 6.78%, although above the goal, decreased very significantly compared to the previous year, which was 14.8% (Table 1).There were 9 cases of grade IV phlebitis and no cases of grade VI, which improved compared to the previous year where the cases that occurred were a reason for patient readmission.92.3% of phlebitis was classified between grades I and II, which is within what was expected;This means that the presence of phlebitis is detected very early.The services that had the most phlebitis in relation to the canalized veins were, in order, the MICU, the PICU, the CICU and the 2nd floor of hospitalization.
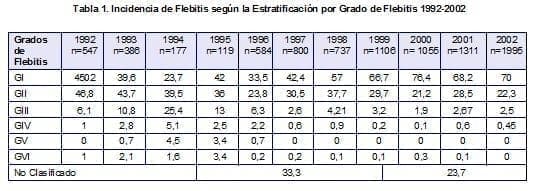

The medications that contribute to a greater degree to the presence of phlebitis are, in order, the antibiotics such as Levofloxacin, vancomycin and ciprofloxacin, being responsible for 36% of phlebitis.Medications such as amiodarone, dopamine and nitroglycerin have been shown to cause a high degree of phlebitis and despite being known by doctors, they continue to be used peripherally.(Table 2)


2.1.3.Bacteremia secondary to Central Venous Catheter (CVC)
During the year, 1,169 central venous catheters were inserted in 937 patients for a total of 1.2 catheters per patient.Of the total catheters, 171 (14.6%) correspond to nursing, being the third group in insertion volume after Anesthesia and Internal Medicine.(Table 3)
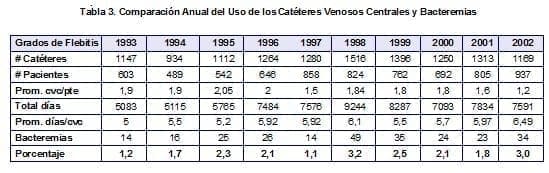

The number of patients increased compared to the last five years, however the average number of catheters per patient decreased significantly. patient, in accordance with the modification in the management guide for central venous catheters, in which the catheter is changed only if a mechanical problem occurs or there is suspicion of infection.Bacteremia secondary to these catheters increased (3.0%) compared to the previous year (1.8%).
These results suggest a revision of the guideline regarding the permanence time of the catheters. catheters and the type of PICC that has been used.
2.1.4 Infection of the surgical wound
Telephone follow-up was carried out at 15 and 30 days after the patient’s discharge to 6073 surgical procedures (99.1% of the total population), of which 109 (1.79%) presented surgical site infection (SSI), compromising the superficial incisional tissue in 54, 1%, deep incisional in 13.8% and organ and space in 32.1%.Clean wound infection, which reflects the quality of care, remained within the parameters (1.13%).(Table 4)
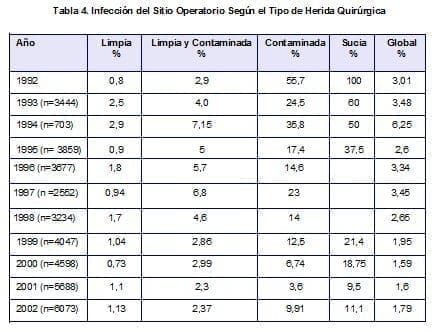

The risk factors for SSI identified in order of frequency were smoking (34.9%), hypertension arterial (22.9%), cancer (19.3%), obesity (13.8%), coronary heart disease (9.2%), Diabetes (6.4%), corticosteroids (3.7%), having Keep in mind that there are patients with more than one associated risk factor, which increases the probability of infection.
2.1.5 Incidents in nursing care
Since 1993, the nursing department created the nursing care quality committee, which weekly analyzes all the problems that arise with nursing care.The information obtained represents the most relevant diagnostic tool to direct staff training efforts, which in the first instance is aimed at solving weaknesses in staff knowledge and skills.This year, 230 incidents were received, corresponding to 1.9% of the total discharges at the institution (n=11,699), a figure that is lower than the previous year (2.69%).The number of incidents in relation to the hospital stay of the patients treated has always been less than 2%, which is the established goal.In 1997 it was 0.32%, in 1998 it was 0.39%, in 1999 it was 0.74%, in 2000 it was 0.72%, in 2001 it was 0.64% and in 2002 it was 0.45. % (n=50006 days stay).The largest incidents are concentrated in administrative errors 29%, basic care 25.6% and medications 16%.Regarding administrative errors, the main one is the identification of samples and paperwork (n= 27; 39.7%).In basic care, the displacement of probes, catheters (n=11; 18.3%) and non-compliance with process protocols (n=9; 15%) and in medication administration is the omission in the registry (n=6, 18). .75%).
The severity of the incidents are classified on a scale from I to V, with one being the least serious and five being the most;the maximum degree represents a high risk to the patient’s life or an unethical act by the person responsible.81.9% of the incidents are between grade one and two, which implies that the patient did not present any alteration in her condition.3.8% grade III, where the patient presents physiological alteration but which did not merit intervention.The remaining 14.2% correspond to cases in which the patient required nursing or medical intervention to correct the problem.
2.1.6 Wound and Ostomy Clinic
Since the opening of this clinic in May 2001, the care of ostomy patients and patients with surgical wounds was centralized, management criteria were unified based on management guides and we have become a national reference center. which is demonstrated in the following table with the increase in the number of patients.(Table 5)
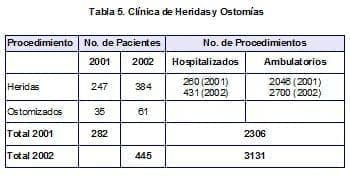

445 patients were treated for a total of 3131 procedures, including outpatients (86.2%) and hospitalized patients ( 13.8%) The average number of sessions per patient is seven and the daily average number of patients is 22.Additionally, we participated in the organization and creation of the National Association of Nursing Professionals for Wound Management, with the coordinator of this clinic currently serving as president.
2.1.7.Loss of instruments
Since 1999, controls in the processes of receipt and delivery of instruments have been standardized, with the name of the person responsible and, in the event of the loss of a surgical piece, its immediate replacement by the person responsible.This year, of 10,267 procedures performed in surgery rooms, only 4 surgical pieces were lost and replaced.
2.2 Personnel indicators
The organizational climate is a determinant of service quality since the importance of the satisfaction of operational personnel and their working conditions cannot be underestimated.As Peter Drucker says “the central axis of good management is people.”Giving them power, involving them in plans, goals, problem solving, taking their proposals into account and analyzing them makes them people committed to the institution, thus facilitating the fulfillment of the objectives.For this reason, two indicators that may reflect the organizational climate are closely evaluated.
2.2.1 Personnel Turnover
The turnover of Personnel is perhaps the factor that most affects the quality of nursing care since it makes it difficult to standardize processes, achieve improvements, and maintain continuity in education programs.This year, 22 people retired from the Nursing Department, of which 15 are professional nurses, 6 nursing assistants and one assistant, constituting a global turnover percentage of 5.9%, which is lower than last year (6.24%).(Table 6)
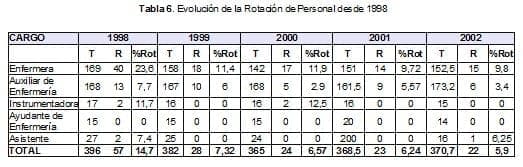

The greatest cause of resignation continues to be the economic factor in professionals (66.6%) and in auxiliaries.Retirement to carry out rural work (50%).
Of the department’s staff, 15.6% (n=57) work in another institution, which implies that they work double shifts daily.Specifying by positions, 28.8% (n=41) correspond to professional nurses, 6.5% (n=11) assistants, 31.5% (n=5) instrument technicians.What this shows is that there is an urgent need to supplement their income and in turn compromises performance within the institution to a certain extent.
2.2.2.Absenteeism from work
Staff absences are attributed to one of three causes: medical incapacity, calamities or unjustified absences.This year, a total of 724 absent people were registered with a total of 5,080 days of absence, of which 74.2% were disabilities, 19.5% calamities, 3.3% unjustified absences and 3.0% maternity leaves.The total number of absences increased from 638 in 2001 to 724 in 2002. Unjustified absences, which are the only controllable variable, started at 34.2% in 1997 and dropped to 3.3% this year (table 7).Auxiliary staff are the ones with the most absences (373), representing 51.5% of them, followed by nursing professionals (242), assistants (47), helpers (35), instrument technicians (27), and secretaries. (0).Daytime absenteeism is higher (421) than nighttime absenteeism (303).


Taking into account maternity leaves (22) and For other absences, the average number of people absent per day is 13.9, which is slightly higher than the previous year, which was 12.4%.
2.2.3.Among the parameters evaluated for nurses, the following were taken into account: greeting the patient, identification and communication to the patient of the person in charge, review of the venipuncture site, labels of intravenous liquids, drip and frequency of the liquids to be infused, catheters, drains, tubes, irrigations and dressings, wounds and/or skin lesions, obtaining an overall result of 75.4% compliance.
For the auxiliaries, the evaluation focused on the same first three criteria plus the use of recyclable paper for your notes, punctuality in delivery, review of bed rails, doorbell, duck, pisingo, fanny pack, telephone, remote control, state of the bathroom and dressings, wounds and/or skin lesions.The overall percentage was 82.6%, which improved for both cases since the first evaluation.
2.2.4.Performance evaluation
Performance evaluation was carried out on all members of the department, providing objective support for behavior, performance and aspects to improve.
2.2.5.Distinctions in nursing
In recognition of performance, punctuality and interpersonal relationships, a semiannual award is held by voting for the best people within these categories.Additionally, the Emergency Department has its own internal recognition system for nursing staff.These activities have been widely accepted and represent an important stimulus for staff.
2.2.6.Medication administration process
The medication administration process was redesigned which eliminated the drug card, producing savings of $168,000 per month ($2,016,000/year).The most important thing about this change is the preparation towards the digital process.
3.Voice of the customer
3.1 User satisfaction
In health, the satisfaction of fair expectations of users users is one of the dimensions of quality.User satisfaction with nursing care is evaluated through the satisfaction survey of inpatients and outpatients tabulated by the Management Support Unit (UAG), and through quality rounds that are carried out weekly. with the UAG.Of the four items evaluated, satisfaction is above the planned goal, 95%, except for the response to the bell.Absenteeism is undoubtedly a factor that influences the delay in responding to patient requests.Complaints or observations resulting from this process and nursing rounds are analyzed individually by the respective service.
4.Standardization
4.1.Management guides
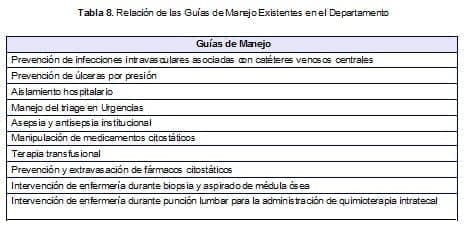
The application of practice based on scientific evidence and the redesign of processes strengthen the quality assurance systems of nursing services.For this reason, the transformation of care protocols to management guidelines based on scientific evidence was continued, with 10 at the end of the year (table 8).The other protocols were fully updated.

5.Education and academic activity
In order to contribute to the professional development of staff, several strategies were developed throughout the year.
5.1 Nursing Update Magazine
It is published quarterly with distribution of three thousand copies per issue;national and international distribution.With the Congress, the 5 years of the magazine were published on a CD-Rom.It is currently available in full text on the Internet and is in the indexing process to be published in Scielo.Nowadays it has become a mandatory text for nursing faculties.
5.2 Induction
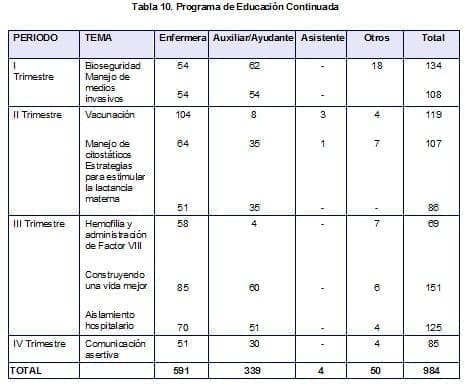
There is a formal induction program to the Nursing Department that takes place every fifteen days for a duration of two weeks, of which five days are for the general introduction of the department’s norms and policies, and general protocols, and the rest in the assigned service.Nine topics were reviewed in 39 sessions over 10 months.Attendance was 96.4%, which increased compared to the previous year (87.9%).(Table 10)

The satisfaction of those attending continuing education is 98% for the exhibitors, the applicability of the topic and audiovisual aids.The time continues to be the one with the greatest dissatisfaction (95.2%) mainly due to the delay in the development of the topic and the start of the talk.
5.4 Scientific meeting
This year, the fortnightly scientific nursing meeting began with exclusively clinical topics, each in charge of a service, with the attendance of 1,153 people, of which 557 were nurses, 554 assistants, 8 floor assistants and 34 people from other positions or services.At this meeting, 22 topics were reviewed.The result was very positive since the participation of all services was achieved with a review of frequent or complex topics from the point of view of nursing management.
5.5 Theoretical courses -Practical for internal and external staff
These constitute the department’s source of financing for staff training.This year only the VI Course on Surgical Wounds and Ostomies was held since all the effort was focused on the holding of the I National Congress of Clinical Nursing Professionals and the VIII Symposium on Nursing Updates (participation of 900 people): within this The “Santa Fé Foundation Nursing Award” was given for Clinical Research and Recognition to two nurses Nelly Garzón and Inés Durana for their contribution to nursing in the country and to Doctor José Félix Patiño for his contribution to clinical nursing.
5.6 Extramural courses and conferences
During the year there were 272 requests for funding to attend extramural courses and conferences and 164 requests for free time to attend, which is more than the previous year.Full funding was granted to 54.4% (n=148) and partial funding to 28.6% (n=78).In terms of time, it occurred every day of the event 22.5% (n=37) and partial 46.9% (n=77).In relation to the previous year, funding increased but the approval of full time to attend the event did not.The investment of money in this area decreased from $11,106,009 to $7,346,348.
5.7 Practice fields for students
91 people were received, including undergraduate students of nursing, surgical instrumentation, nursing assistants and productive stage: Fundación Universitaria del Area Andina (9), UDES (18), SENA (5), Universidad Nacional (48), Usesalud (6).Five students from the Javeriana University in their last semester of nursing received their management practice.Four critical care students received postgraduate studies in the area of Metabolism and Nutrition.
5.8 Professional development
Of the ten assistants awarded scholarships by the institution, six finished their professional nursing careers and four of them were promoted within the institution.The remaining two were given the opportunity to replace December nursing vacations to evaluate their performance.
5.9 Participation in the Faculty of Medicine of the Andes-FSFB
Being aware that with the opening of the faculty the first contact that students will have at the university hospital is with the nursing staff, an intense program was developed, to be developed in in 2003, retraining of all nursing staff from basic concepts to systems specialized in order to ensure a high scientific level.Additionally, with the review of the curriculum, the responsibility of the nursing department in teaching students throughout the degree was made clear.
5.10 Research
An investigation was initiated to identify risk factors that influence the presence of phlebitis.Initially, the information collection format was adapted to begin the investigation as such during this year.
5.11 Other activities
1.Appointment of two nurses specialized in Bioethics as Magistrates of the National Ethics Court, Bogotá and Cundinamarca section
3.Retraining of the transplant coordinator and the head of the nursing department in liver transplant coordination in Birmingham, England.
4.Appointment of the Metabolic and Nutritional Support nurse as General Director of the Interdisciplinary Course on Clinical Nutrition of the Latin American Federation of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (FELANFE).
5.Appointment of the Metabolic and Nutritional Support nurse as President-elect of the Ibero-Latin American section (ILAS) of the American Association of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition (ASPEN).
6.Outpatient services
6.1 Breastfeeding program
As a guideline from WHO and the Ministry of Health, the project to promote breastfeeding was developed as an institutional policy.For its implementation, a training program was carried out for all nursing staff of said services.This year, 60% of exclusive breastfeeding of newborns was achieved, whereas previously 90% of newborns were complemented.The goal continues to be to achieve at least 80% exclusive breastfeeding for newborns.
6.2 Institutional psychoprophylactic course
As of March 2001, it became institutional coordinated by the departments of Nursing, Gynecology, Obstetrics and Pediatrics.Patient coverage went from 5.2% (n=61) couples in 2000 to 9.9% in 2002 (n=138 couples).The users rated it as excellent in 85% and as good in 25%.
6.3 External consultation
It was carried out monitoring of the hemophilia program (14 patients), TB (15 patients), vaccination of the newborn only 20, since this service was subcontracted with the Tercer Milenio group.In adults, 1,182 were vaccinated, which includes two vaccination campaigns against measles and influenza, multiple nursing activities were carried out such as ear washing, injections, removal of stitches, blood pressure measurement, ear piercing, enemas and cytology follow-up.Significant efficiency was achieved in the use of the offices, achieving an occupancy rate of 97%.In the communications area, there was a problem of telephone congestion, permanently causing calls to be returned to the switchboard (2001=2950), which was solved with the increase of a line for Outpatient Consultation and an additional person exclusively for this purpose.
6.4 Hypertension and Diabetes Clinic
In conjunction with the Department of Internal Medicine, this clinic was opened, fully complying with the expectations and in March it was complemented with the guided gymnastics program.In nursing consultation, 923 hypertension patients were treated with 3554 activities, 447 Diabetes patients with 1490 activities and 147 combined.36 educational talks on hypertension and 33 on Diabetes were given.In the therapeutic gymnastics program, 1,317 patients were treated compared to the previous year, which was 525 for a total of 3,157 sessions.The annual course for patients and families was held with 196 attendees for hypertension and 186 for diabetes.Due to the increase in patient volume, another part-time nurse was appointed who received the formal diabetes training course.
6.5 IOCAL Oncology Institute
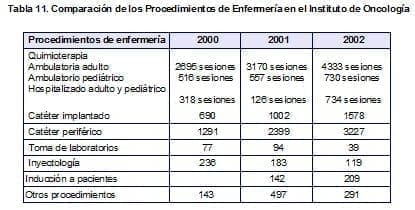
Outpatient chemotherapy procedures increased by 1,163 sessions basically at the expense of pediatric patients, due to the transfer of the pediatric oncohematology unit, as well as in hospitalized patients, where it increased by 781 sessions of chemotherapy.(Table 11)

Conclusions
The Nursing Department is clear that the effort to improve quality and efficiency in health systems is one of the contemporary imperatives.For this purpose, it has been based on comprehensive quality management in which, with the use of quality indicators, it is easy to understand what is happening and why it is happening in the different services, as well as allowing us to plan future development. of the area, program existing resources in the best possible way and periodically evaluate the results obtained with the proposed modifications after analyzing the problems.This comprehensive approach allows for a proactive rather than reactive attitude in the management of the Department.
Thanks to teamwork and the empowerment granted to its members, the growth and recognition of the department has been allowed both at the intra and extramural and the achievement of successful results in many of the recurring problems.
Bibliography
1.Giacometti, L.F.Entrepreneurship of Public Hospitals: The International Experience. 1999.
2. PAHO, WHO.Development of Standardized Nursing Information Systems.2001
3. PAHO, WHO.Nursing Services to Contribute to the Achievement of Equity, Access, Quality and Sustainability of Health Services.2001.
.